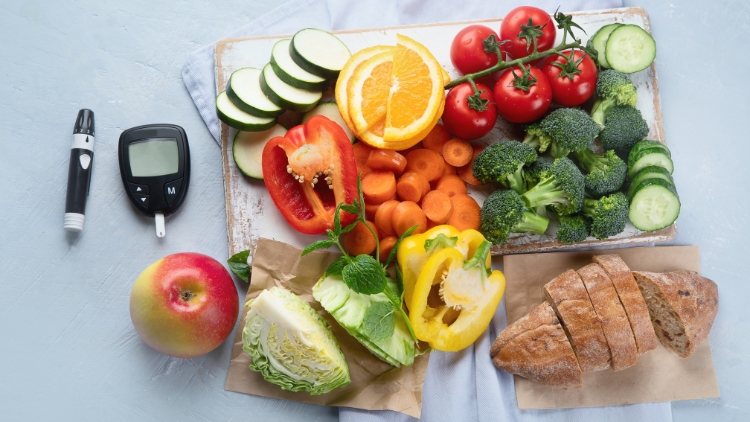
Diabetes, often referred to as the ‘silent killer,' is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While awareness about diabetes has grown, unfortunately, so have the misconceptions surrounding it. In this article, we will debunk 10 common myths about diabetes, empowering you with accurate information and fostering a better understanding of this complex condition.
Myth 1: Diabetes Is Caused by Eating Too Much Sugar

- Let's clear up the confusion: while excessive sugar intake can contribute to weight gain and other health problems that increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, it's not the sole culprit.
- The primary cause of type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune reaction where your body mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas.
- Type 2 diabetes develops when your body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough of it. Several factors contribute to this, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
- So, while cutting back on sugary treats is a healthy choice for everyone, it's important to understand the broader picture when it comes to diabetes.
Myth 2: People with Diabetes Can't Eat Sweets or Carbohydrates

- It's time to break free from this restrictive mindset! People with diabetes can absolutely enjoy sweets and carbohydrates as part of a balanced diet.
- The key is moderation and making informed choices.
- Counting carbohydrates, understanding portion sizes, and monitoring blood sugar levels are crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
- With the right knowledge and support, you can still savor those occasional treats without compromising your health.
Myth 3: Only Overweight People Get Type 2 Diabetes

- This misconception can be harmful as it can lead to a false sense of security for individuals who are not overweight.
- While being overweight or obese does increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, it's not the only factor.
- Genetics, family history, ethnicity, and lifestyle choices all play a significant role.
- Even individuals with a healthy weight can develop type 2 diabetes.
Myth 4: Diabetes Is Not a Serious Condition
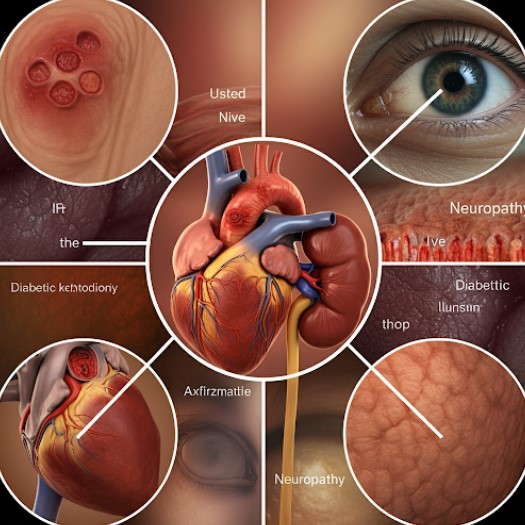
- Let's set the record straight: diabetes is a serious chronic condition that, if not managed properly, can lead to a range of complications.
- These complications can affect various parts of your body, including your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and feet.
- In some cases, these complications can be life-threatening. According to the World Health Organization, diabetes was the direct cause of 1.5 million deaths in 2019.
- However, the good news is that with proper management, including a healthy lifestyle, regular monitoring, and medication when necessary, you can significantly reduce your risk of complications and live a long, fulfilling life.
Myth 5: All Types of Diabetes Are the Same

- There are actually several different types of diabetes, each with its own unique characteristics and causes.
- The most common types are type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where your body attacks the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas, requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 diabetes develops when your body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough of it. Lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin may be needed for management.
- Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Understanding the different types of diabetes is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.
Myth 6: People with Diabetes Can't Exercise
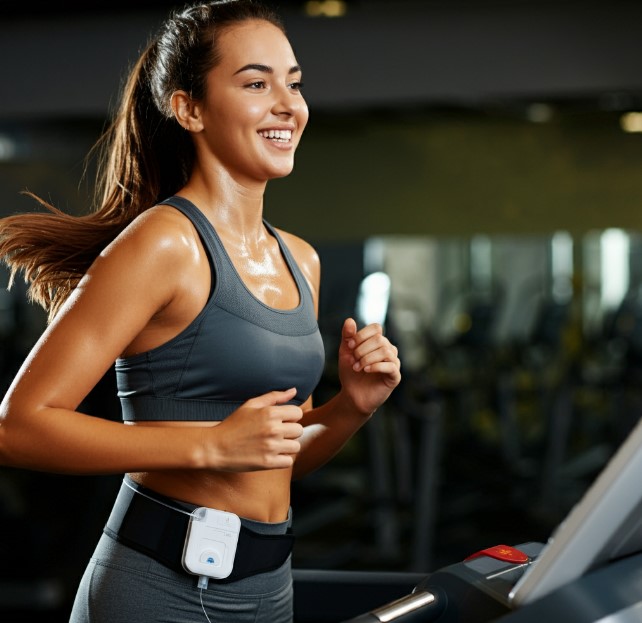

- On the contrary, regular physical activity is essential for people with diabetes.
- Exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity, control blood sugar levels, manage weight, and reduce the risk of complications.
- It's important to consult your healthcare team to create an exercise plan that's safe and suitable for you.
- They can advise you on the best types of activities, intensity levels, and precautions to take.
Myth 7: Insulin Is a Cure for Diabetes

- While insulin is a life-saving medication for people with type 1 diabetes and some individuals with type 2 diabetes, it's not a cure.
- It's a hormone that helps your body use glucose for energy.
- People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to replace the insulin their body doesn't produce.
- Some people with type 2 diabetes may also need insulin therapy if other medications and lifestyle changes aren't enough to manage their blood sugar levels.
Myth 8: If You Have a Family History of Diabetes, You'll Definitely Get It

- Having a family history of diabetes does increase your risk of developing the condition, but it doesn't guarantee that you will get it.
- You can significantly reduce your risk by adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise.
- It's also important to get screened for diabetes regularly, especially if you have other risk factors.
Myth 9: People with Diabetes Are More Prone to Infections

- It's true that high blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making it slightly harder for your body to fight off infections. However, this doesn't mean people with diabetes are inherently more prone to infections than others.
- The key is managing blood sugar levels effectively and practicing good hygiene. Studies have shown that maintaining optimal blood sugar control can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Myth 10: Diabetes Is Only a Problem for Older Adults
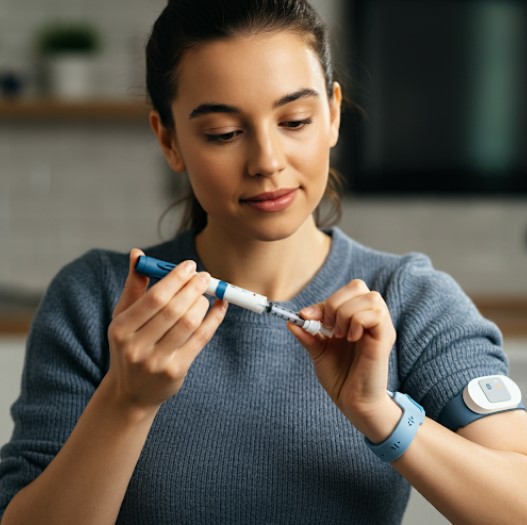

- While type 2 diabetes is more common in older adults, it can affect people of all ages, including children and young adults.
- In fact, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in young people has been increasing in recent years, likely due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles.
- It's important for everyone, regardless of age, to be aware of the risk factors for diabetes and take steps to prevent it.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex condition, but it's manageable. By dispelling these common myths and arming yourself with accurate information, you can take control of your health and live a full and active life. Remember, knowledge is power. Don't let misconceptions hold you back. Seek reliable information, work closely with your healthcare team, and embrace a healthy lifestyle.
Remember these key takeaways:
- Diabetes has various causes and types – It's not just about sugar intake.
- Healthy eating is key – Focus on balanced meals, not restrictions
- Exercise is beneficial – Find activities you enjoy and stay active.
- Management is possible – With the right tools and support, you can thrive.
If you have concerns about diabetes, reach out to your doctor for personalized advice. You're not alone in this journey. Millions of people are successfully managing diabetes and living fulfilling lives. With the right knowledge and support, you can too.
References
- Sugar-sweetened beverages and risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019
- Lean diabetes mellitus: An emerging entity in the era of obesity
- Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus
- Physical activity/exercise and diabetes: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association
- The Burden of Diabetes in the United States: 2015–2020
- Effect of intensive lifestyle intervention on sustained weight loss and long-term cardiovascular outcomes in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes: 10-year results of the Look AHEAD trial
- Association of Leisure-Time Physical Activity With Risk for 26 Types of Cancer in 1.44 Million Adults