The first hint of trouble was subtle. A persistent thirst that seemed unquenchable, no matter how much water I drank. Then came the unexpected weight loss, despite a healthy appetite. And finally, the frequent nighttime bathroom trips. These seemingly unrelated symptoms were, in fact, early warning signs of a looming health crisis – a condition called diabetes. It wasn't until a routine doctor's visit and a shocking blood sugar reading that the gravity of the situation truly sunk in. I was on the precipice of a chronic illness that could dramatically alter my life. But there was still hope. By embracing lifestyle changes and a proactive approach, I could significantly reduce my risk and potentially prevent the full-blown onset of diabetes.
This experience sparked a deep desire within me to understand this widespread disease and learn how to fight it. Now, I'm driven to share that knowledge with you. While some risk factors, like family history and genetics, are beyond our control, there are many powerful strategies we can employ to protect our health. This article explores seven key ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes, empowering you to take charge of your well-being and potentially avoid the challenges I faced.
1. Embrace the Power of Movement

In today's world of sedentary jobs and convenient transportation, it's easy to slip into a pattern of inactivity. But our bodies crave movement, and regular physical activity is vital for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. When you engage in physical activity, your muscle cells become more efficient at absorbing glucose from your bloodstream, reducing the demand on your pancreas to produce insulin.
Find Your Fitness Groove
The beauty of exercise is that it doesn't have to be a dreaded chore. Find activities you genuinely enjoy, whether it's dancing, swimming, hiking, or simply taking brisk walks in nature. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Moderate-intensity activities elevate your heart rate and make you breathe harder. You should be able to hold a conversation but not sing during the activity.
- Break It Up: Even short bursts of activity throughout the day can make a difference. Take the stairs instead of the elevator, park farther from your destination, or walk around during phone calls.
- Make It Social: Join a fitness class, find a workout buddy, or participate in team sports to add an element of fun and accountability to your routine.
Boost Your Strength
Don't underestimate the power of strength training. Building muscle mass not only improves your physical fitness but also enhances your body's ability to use insulin effectively. Aim for two to three sessions of strength training per week, targeting all major muscle groups.
- Bodyweight Exercises: You don't need fancy equipment to get started. Push-ups, squats, lunges, and planks are all excellent bodyweight exercises that can be done anywhere.
- Resistance Bands: These portable and affordable tools add resistance to your movements, helping you build strength and endurance. They are ideal for beginners or those exercising at home.
- Weightlifting: If you have access to a gym or weights, incorporate exercises like deadlifts, bench presses, and rows into your routine. This is suitable for individuals looking to build significant muscle mass and strength.
2. Nourish Your Body with a Balanced Diet

The food we consume has a profound impact on our health, and making conscious choices about our diet can significantly reduce our risk of developing diabetes.
Prioritize Whole Foods
Focus on consuming a variety of whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall health.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day. They're packed with antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole-grain bread, pasta, rice, and cereals over refined grains. Whole grains are higher in fiber and nutrients, which help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Lean Proteins: Include lean proteins like fish, poultry, beans, lentils, and tofu in your meals. Protein helps you feel full and satisfied, which can aid in weight management.
- Healthy Fats: Opt for unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats promote heart health and help regulate blood sugar levels.
Limit Added Sugars and Processed Foods
Added sugars and processed foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Read Labels: Be mindful of added sugars lurking in unexpected places, such as sauces, condiments, and packaged snacks.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and avoid excess sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Choose Healthier Snacks: Opt for fruits, vegetables, nuts, or yogurt instead of processed snacks like chips, cookies, and candy.
3. Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Weight

Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdomen, significantly increases your risk of developing diabetes.
Set Realistic Goals
Losing even a small amount of weight can make a big difference in your health. Aim for a gradual and sustainable weight loss of 5-7% of your body weight.
- Focus on Lifestyle Changes: Rather than resorting to fad diets, make sustainable changes to your eating habits and activity levels.
- Celebrate Small Victories: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress along the way, no matter how small.
- Seek Support: Connect with friends, family, or a support group to stay motivated and accountable.
Practice Mindful Eating
Pay attention to your body's hunger and fullness cues. Avoid distractions while eating, such as watching TV or scrolling through your phone, as this can lead to mindless overeating.
- Portion Control: Use smaller plates and bowls to help manage portion sizes.
- Savor Your Food: Take your time to enjoy the flavors and textures of your meals.
- Listen to Your Body: Stop eating when you feel comfortably satisfied, not overly full.
4. Prioritize Quality Sleep

In our fast-paced lives, sleep often gets neglected. But inadequate sleep can disrupt your blood sugar control and increase your risk of developing diabetes.
The Sleep-Diabetes Connection
When you consistently don't get enough sleep, your body produces more stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can interfere with insulin's ability to regulate blood sugar. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and an increased risk of developing diabetes.
Recharge with Restful Sleep
Most adults need around 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Prioritize sleep as a non-negotiable part of your health routine.
- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up around the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate your body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Wind down an hour or two before bed by reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows to promote restful sleep.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: The blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with your sleep. Avoid screens for at least an hour before bedtime.
5. Manage Stress Effectively

Stress is an unavoidable part of life, but chronic stress can negatively impact our health, including our blood sugar control.
The Stress-Diabetes Link
When you're stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase insulin resistance. This means your body's cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Find Your Stress-Busting Strategies
It's crucial to find healthy ways to manage stress and incorporate them into your daily routine.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help you cultivate a sense of calm and reduce stress levels. Even a few minutes of deep breathing each day can make a difference.
- Connect with Others: Spend time with loved ones, join a social group, or talk to a therapist. Social connection can provide support and help you cope with stress.
- Engage in Hobbies: Make time for activities you enjoy, whether it's gardening, painting, reading, or playing music. Hobbies provide an outlet for stress and can boost your mood.
6. Know Your Numbers and Get Regular Checkups
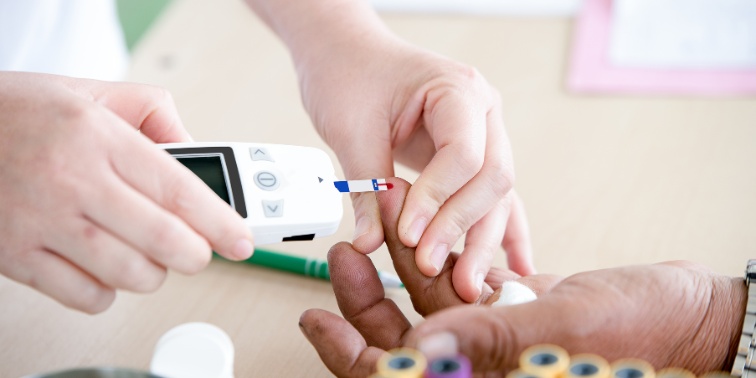
Knowledge is power when it comes to your health. Understanding your risk factors and getting regular checkups can help you stay ahead of diabetes and take preventive measures.
Assess Your Risk
Talk to your doctor about your risk factors for diabetes, such as family history, age, weight, and lifestyle habits. Based on your risk assessment, your doctor may recommend getting your blood sugar levels checked.
Key Tests and Screenings
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test: This measures your blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- A1C Test: This test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: This test measures your blood sugar levels before and 2 hours after you drink a sugary drink.
Regular Checkups: Your Health Ally
Even if your blood sugar levels are normal, it's important to get regular checkups, especially if you have risk factors for diabetes. Your doctor can monitor your health, provide guidance on lifestyle changes, and detect any early signs of diabetes.
7. If Needed, Consider Medication
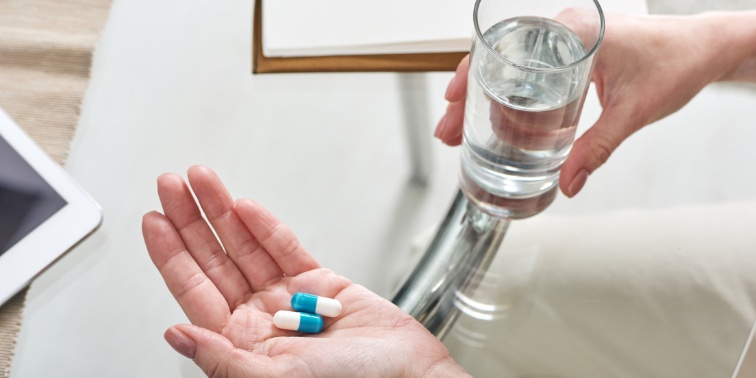
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to prevent diabetes. If your doctor determines that you're at high risk, they may recommend medication to help manage your blood sugar levels.
Medication Options
- Metformin: A commonly prescribed medication for people with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. It works by improving your body's sensitivity to insulin and reducing the amount of glucose produced by your liver.
- Other Medications: Several other medications are available to help prevent or manage diabetes, including SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and DPP-4 inhibitors. Your doctor can help determine which medication is right for you based on your individual needs and health history.
Work Closely with Your Doctor
It's important to work closely with your doctor to determine if medication is right for you. They can assess your individual needs, monitor your progress, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
The journey to prevent diabetes is a marathon, not a sprint. It requires commitment, patience, and a willingness to make sustainable lifestyle changes. But the rewards are well worth the effort. By taking proactive steps to manage your weight, stay active, eat a healthy diet, prioritize sleep, manage stress, and get regular checkups, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes and live a healthier, more fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Reach out to your healthcare providers, family, and friends for support and guidance. Together, we can take charge of our health and prevent diabetes from stealing our vitality.
References
- Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)
- The Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study (DPS)
- The Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study
- Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes)